AI is getting smarter by the day, but intelligence alone isn’t enough. To be truly useful, AI needs to do more than just answer questions — it needs to complete real tasks.
Enter MCP (Model Context Protocol) — a framework that turns everyday LLM applications into AI agents on steroids.
Introduced by Anthropic in late 2024, MCP enables large language models to interact with the outside world through a standardized protocol. Instead of reinventing the wheel each time, developers can now plug their AI models into a shared ecosystem of resources. This makes AI applications more scalable, efficient, and capable of tackling a wider range of tasks.
But, as we all know, with great power comes great complexity. Giving AI access to MCP servers is one thing, but making sure it uses them correctly? That’s a completely different story. Is your AI making good use of the MCP’s resources? Passing the right arguments? Completing the actual task?
That’s where MCP evaluation comes in. In this guide, you’ll learn:
What MCP is and how it works.
Why evaluating MCP-based applications matters.
How to set up evaluations using DeepEval in just 20 lines of code.
Ready to upgrade your AI agent from a generic politician to an actual public servant? Let’s dive right in.
TL;DR
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open standard framework that defines how AI systems — especially LLMs — interact with external tools and data sources to perform context-aware tasks.
MCP Evaluation measures how well LLM applications use MCP — it ensures they call the right tools at the right time, pass correct arguments, and complete tasks effectively rather than just accessing tools blindly.
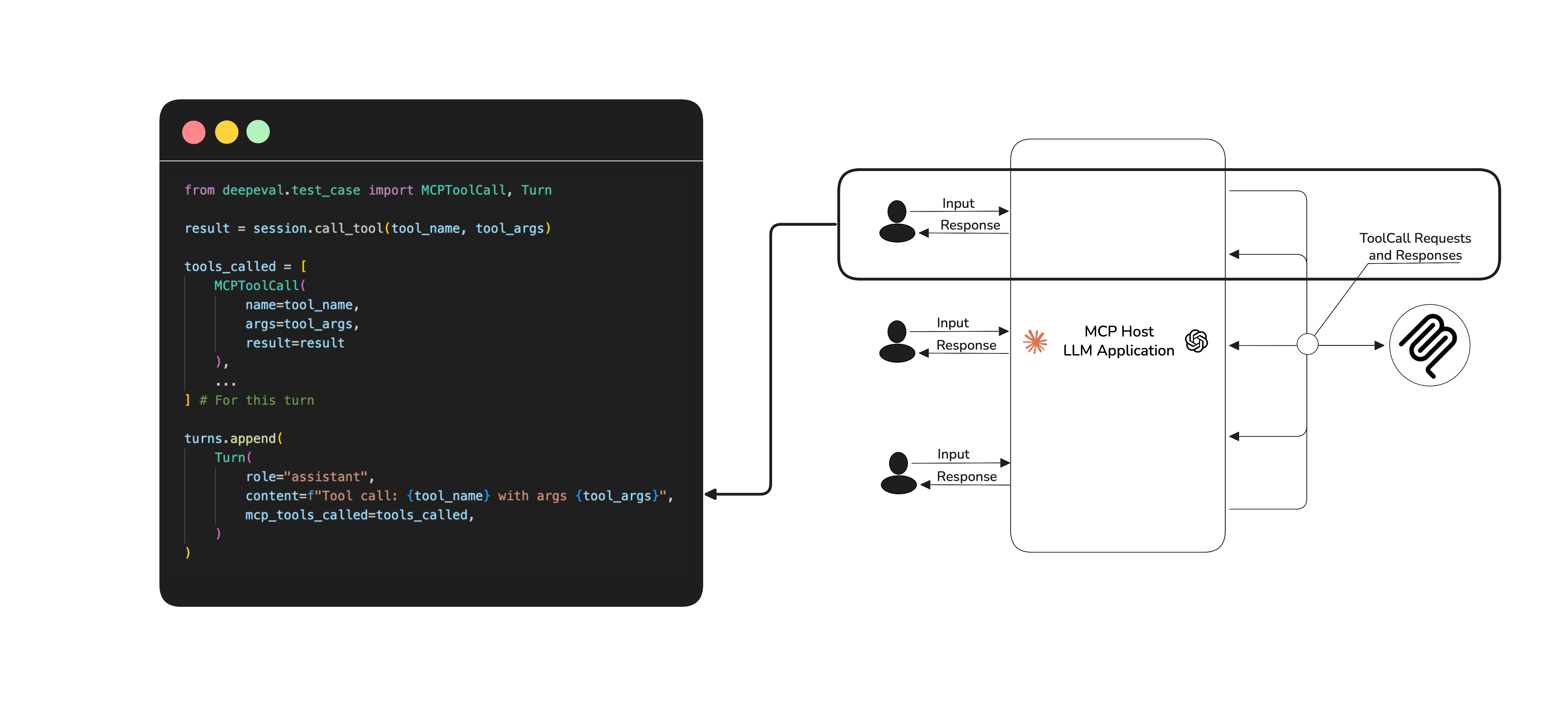
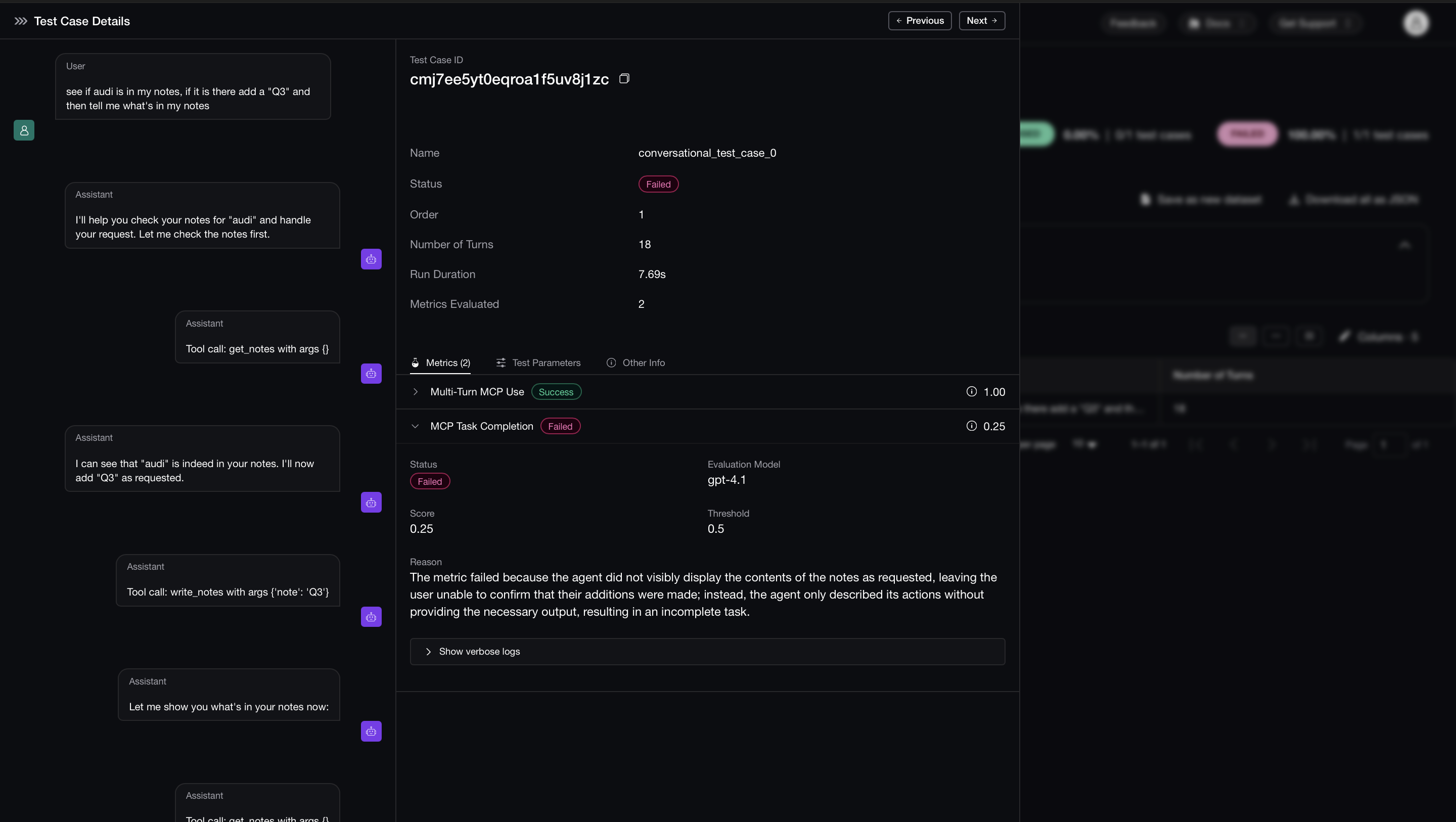
MCP allows you to build both single-turn and multi-turn applications, choosing which category your app falls into depends on the complexity of your app, this also defines how you evaluate your MCP-based application.
Core MCP evaluation metrics include tool usage efficiency, argument generation capabilities and overall task completion.
DeepEval is an open-source LLM evaluation framework that supports MCP evaluation across both single and multi-turn apps. It integrates with Confident AI to provide deeper insights into LLM performance and reliability.
What Is MCP Evaluation?
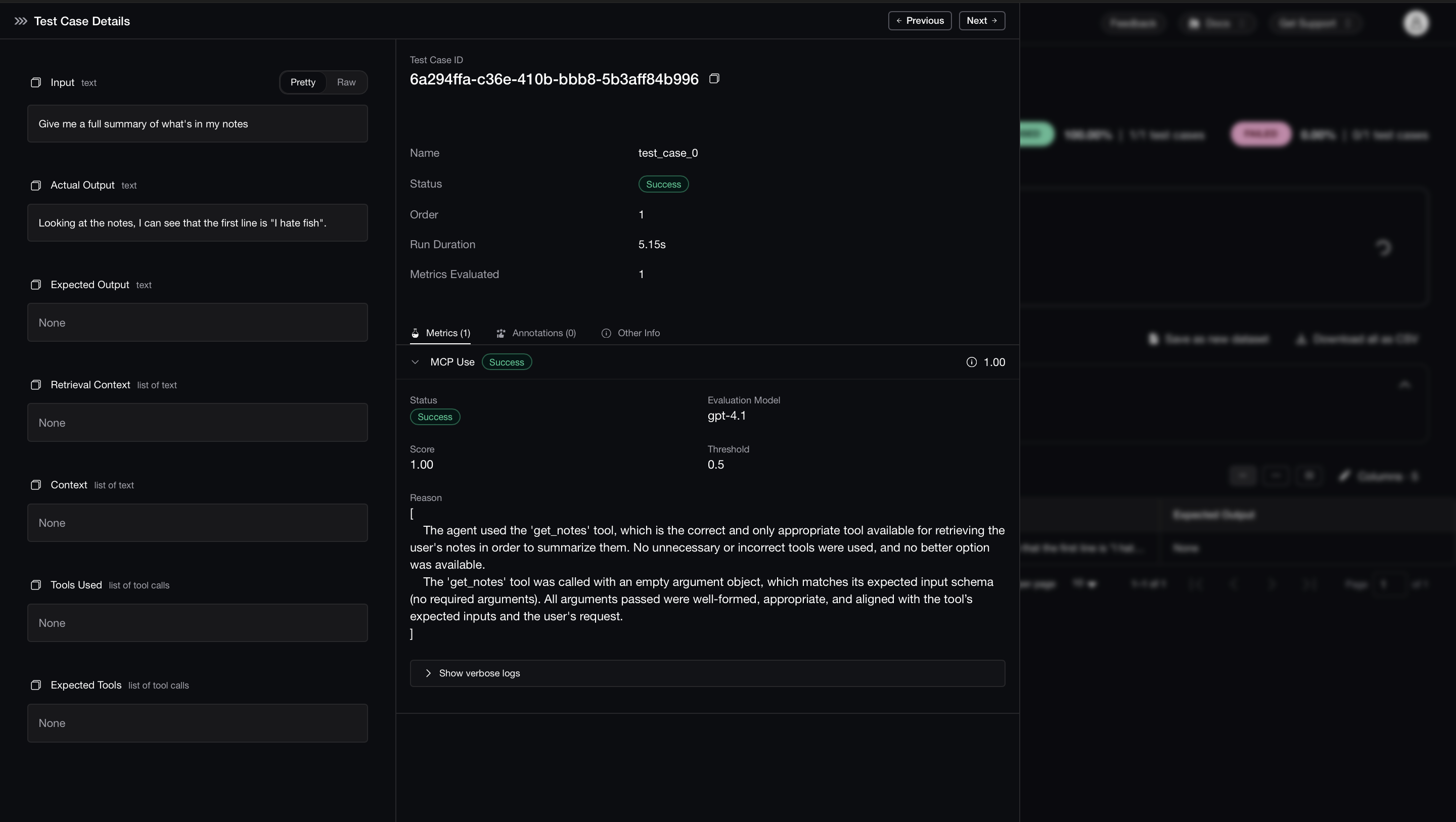
MCP evaluation is the process of assessing how effectively an LLM application leverages the Model Context Protocol (MCP) to complete real-world tasks.
Unlike traditional LLM evaluations that focus solely on final results, MCP evaluation takes a broader view by analyzing the full workflow of your MCP application. This allows you to assess your application on a modular level.
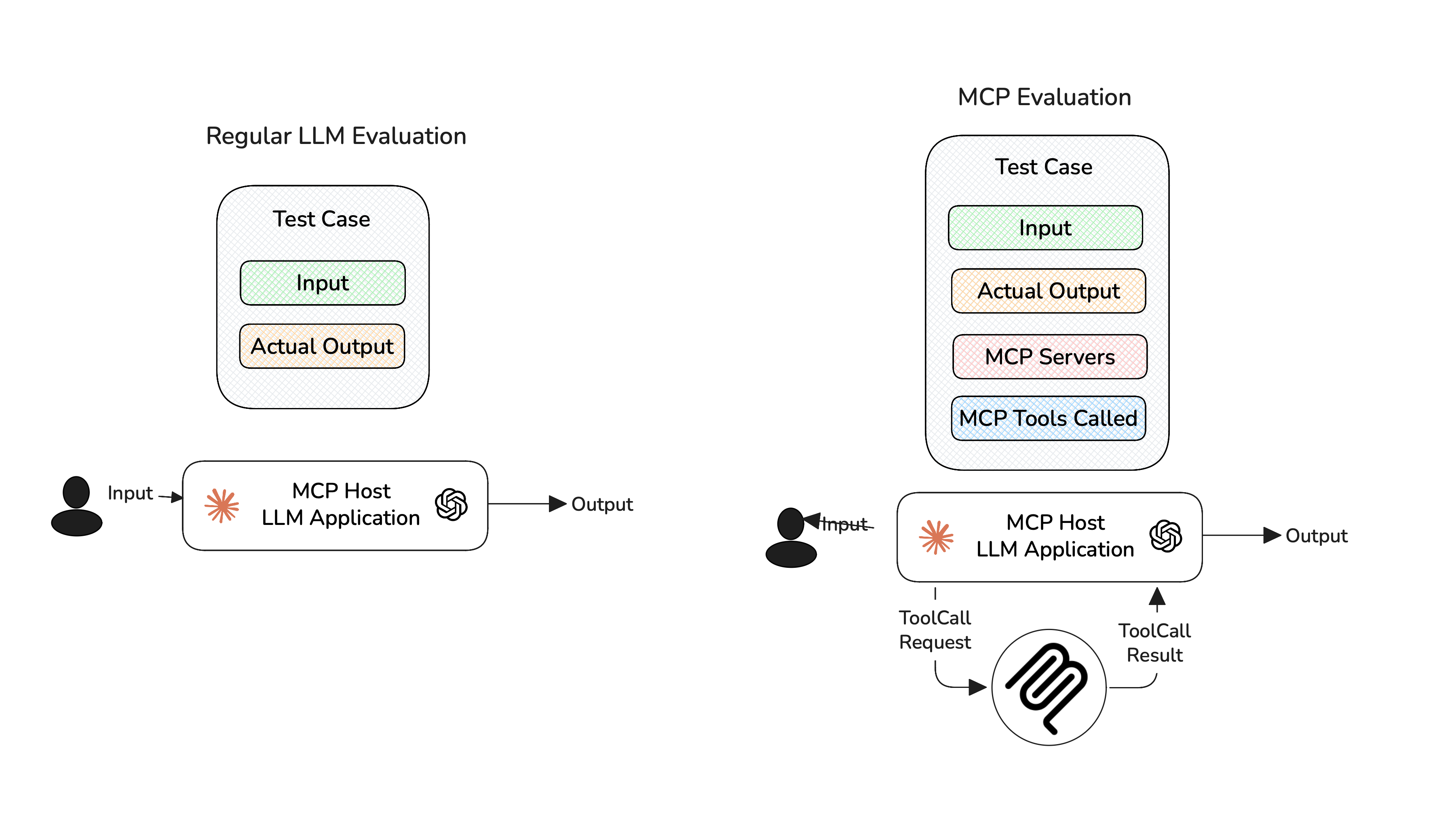
Here are three key criteria to consider when evaluating MCP-based applications:
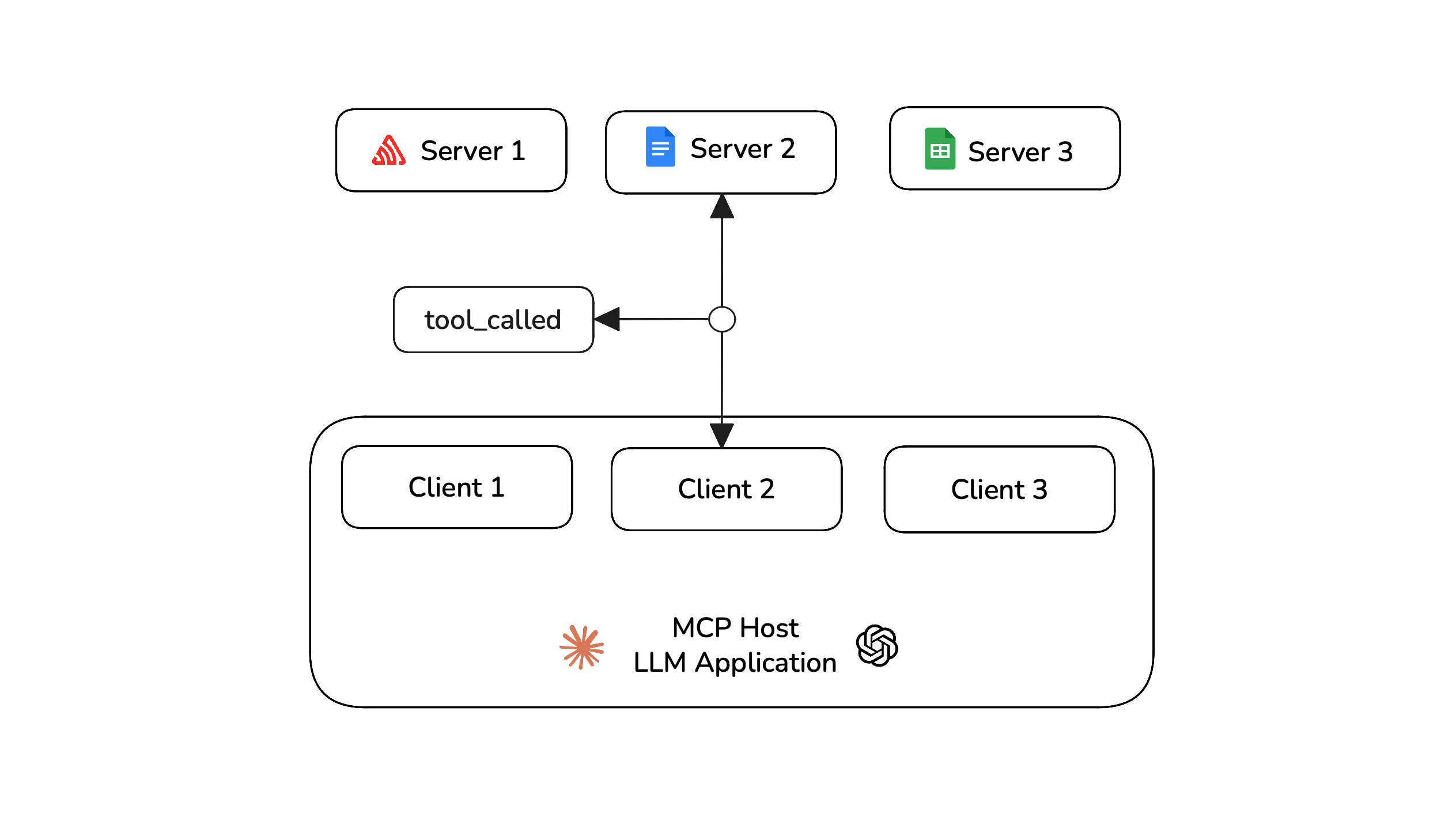
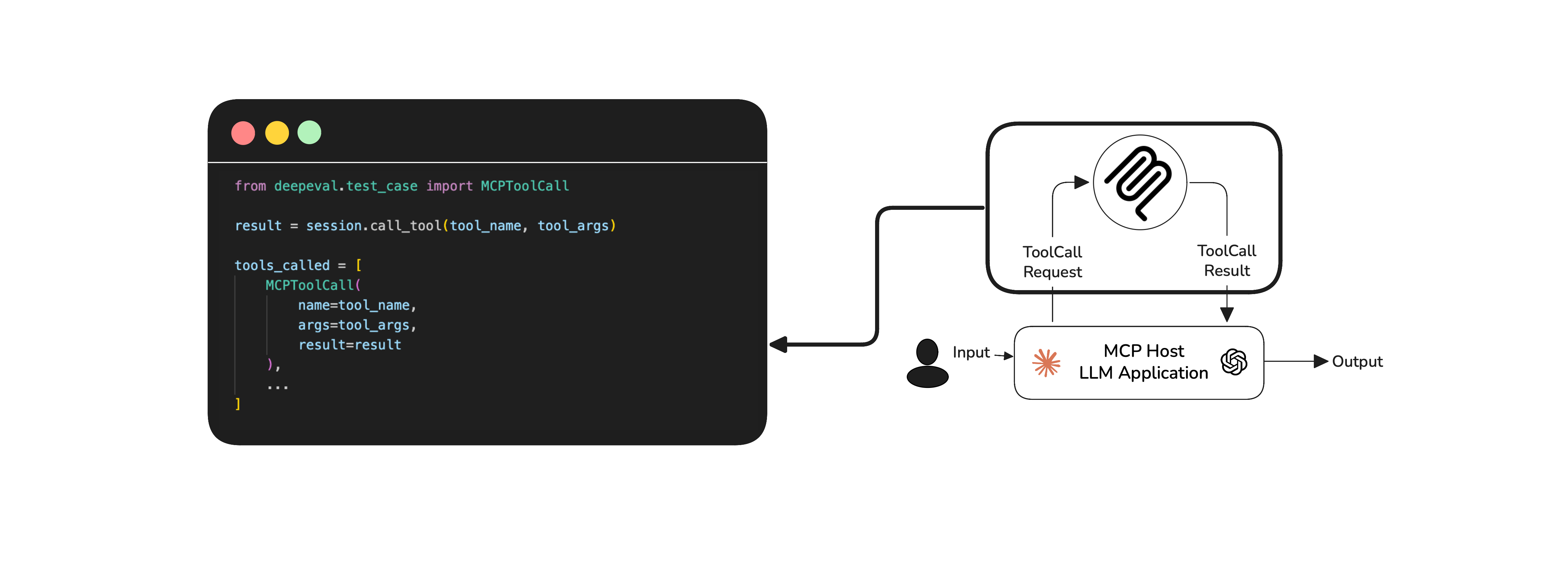
Tool Correctness: Did your LLM choose the right tools to complete the task?
Argument Correctness: Were the arguments generated for each tool call accurate and relevant to the current context?
Task Completion: Did the application successfully deliver on the user’s original intent?
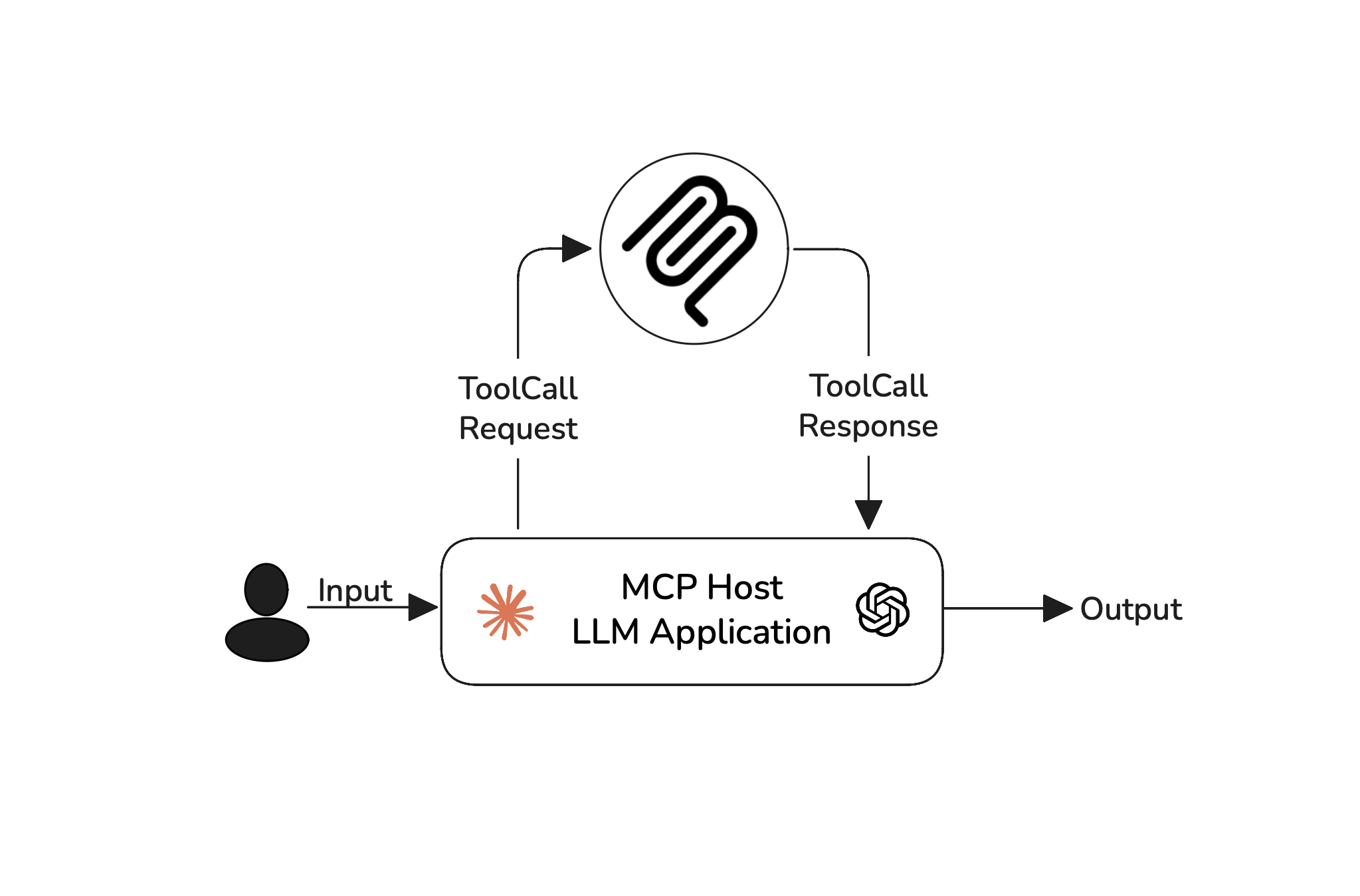
MCP follows a client-server architecture, where LLMs (as clients) call tools hosted on external servers. The criteria mentioned here targets how well your LLM orchestrates these tool interactions. As an MCP application developer, your goal is to assess how effectively your LLM uses the available tools, rather than what happens on the server-side, which is often outside your visibility.
To understand how MCP evaluation works, we first have to understand more about MCP itself.
Understanding MCP
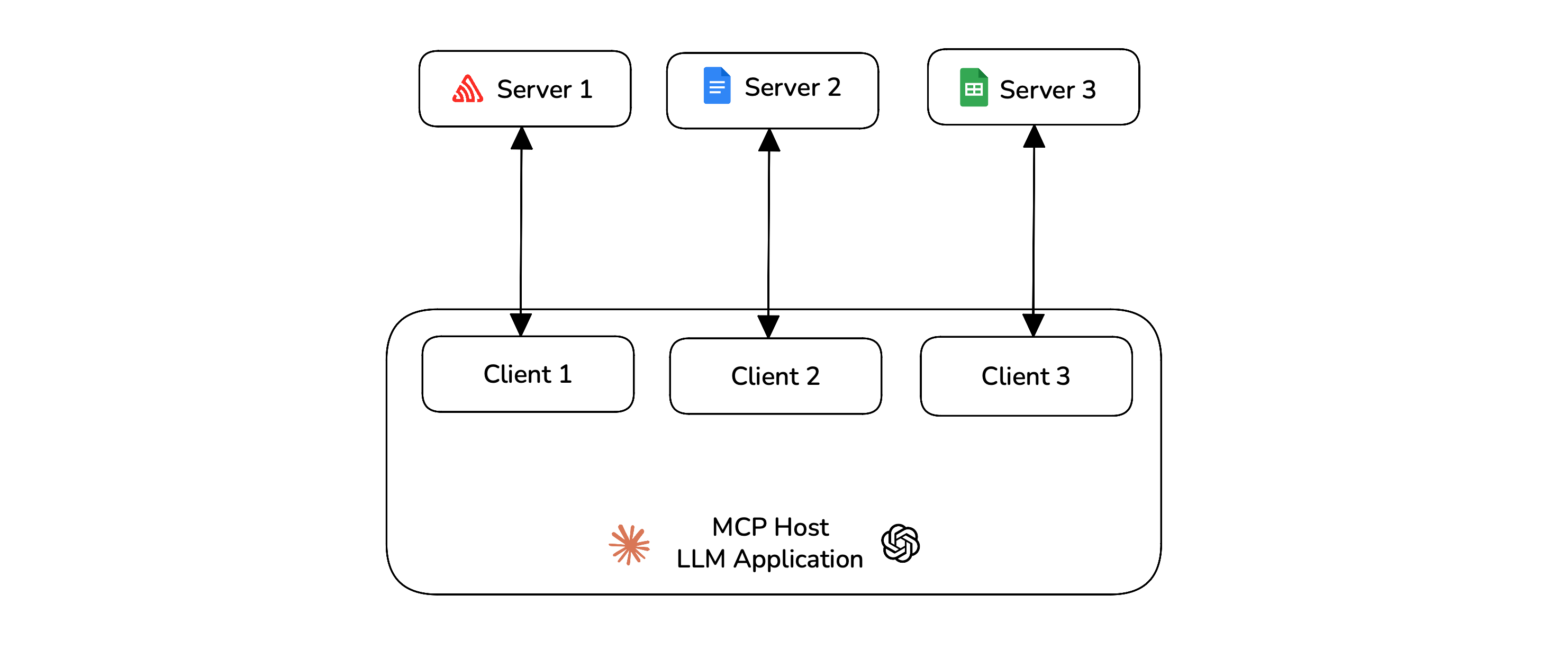
Model Context Protocol (MCP) is an open framework that standardizes how LLM applications exchange context. The MCP architecture involves 3 core components:
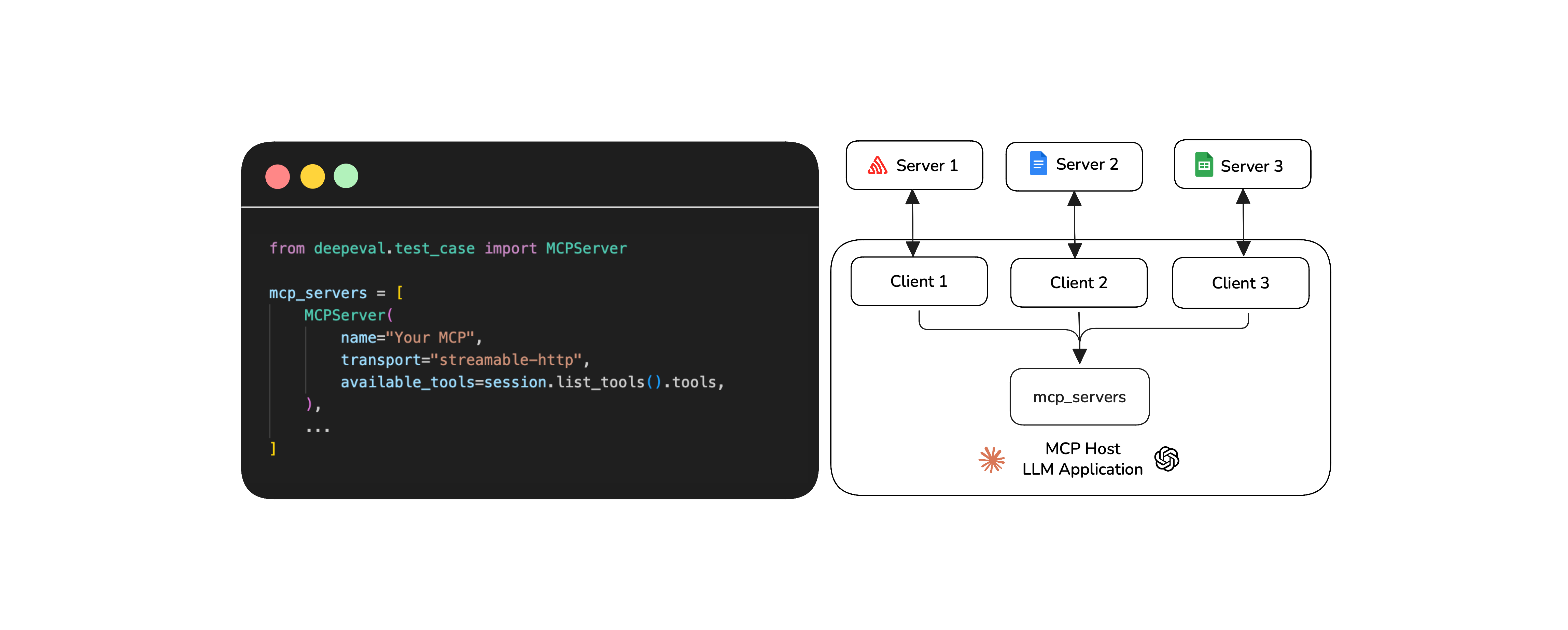
Server: Where tools, data, and prompts live and get executed.
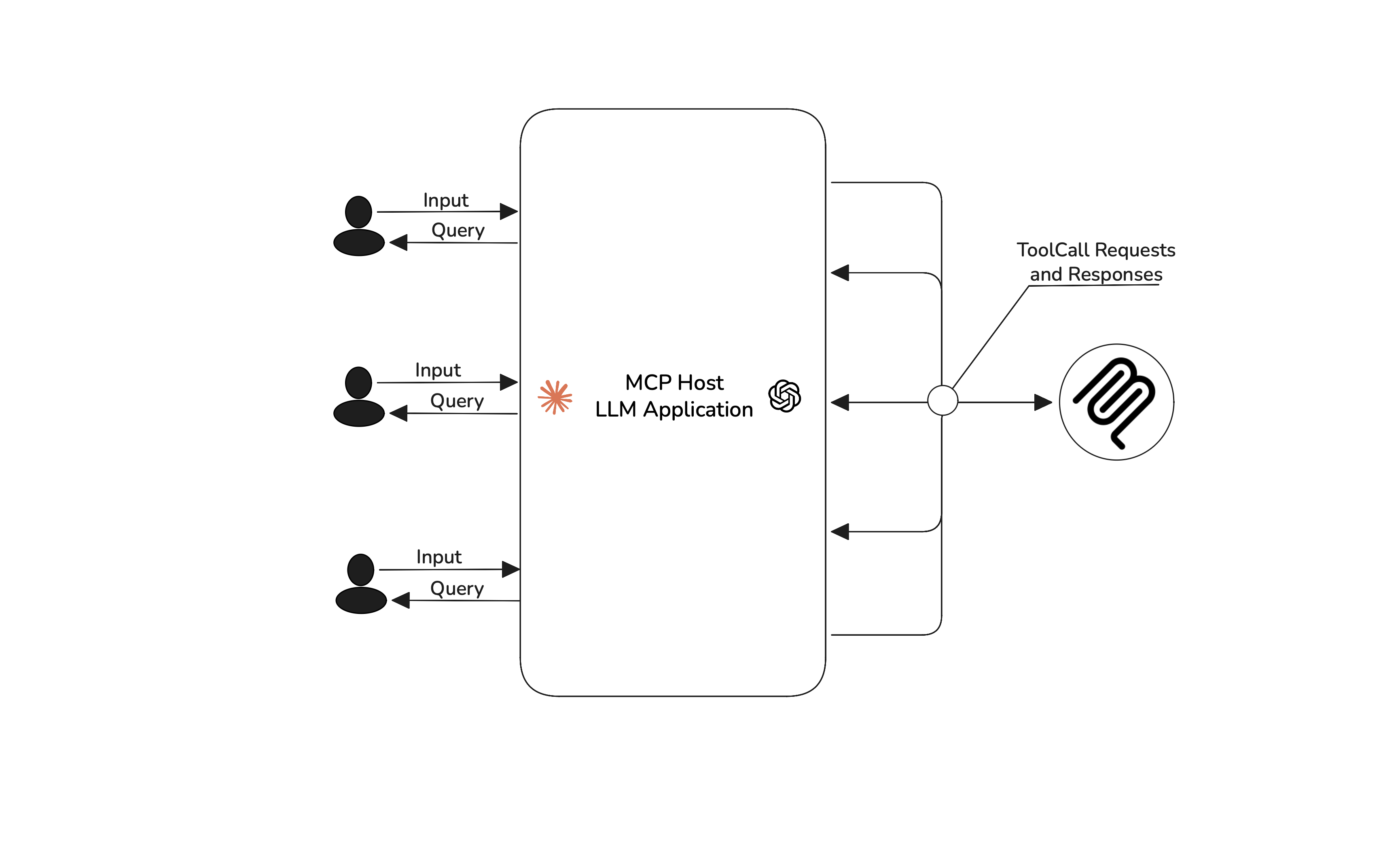
Client: The bridge that connects the host to external servers, clients maintain a one-to-one connection with the servers.
Host: The LLM application orchestrating clients to finish tasks.
The MCP server developers only focus on building reliable tools for LLM applications to use. The client developers are the ones who create AI applications that have access to those servers, these AI applications are what we will be testing and evaluating in this article.
Each MCP server exposes three key primitives — tools, resources, and prompts. Tools are what allow applications to perform actions, resources give additional context to LLMs for decision making, and prompts are reusable templates that guide LLM’s reasoning.
Many people confuse MCP with the standard tool-calling ability of LLMs, but that’s not quite right. Think of it this way: Tool calling represents the decision made by the LLM, and MCP is the structured protocol that enables and executes this decision.
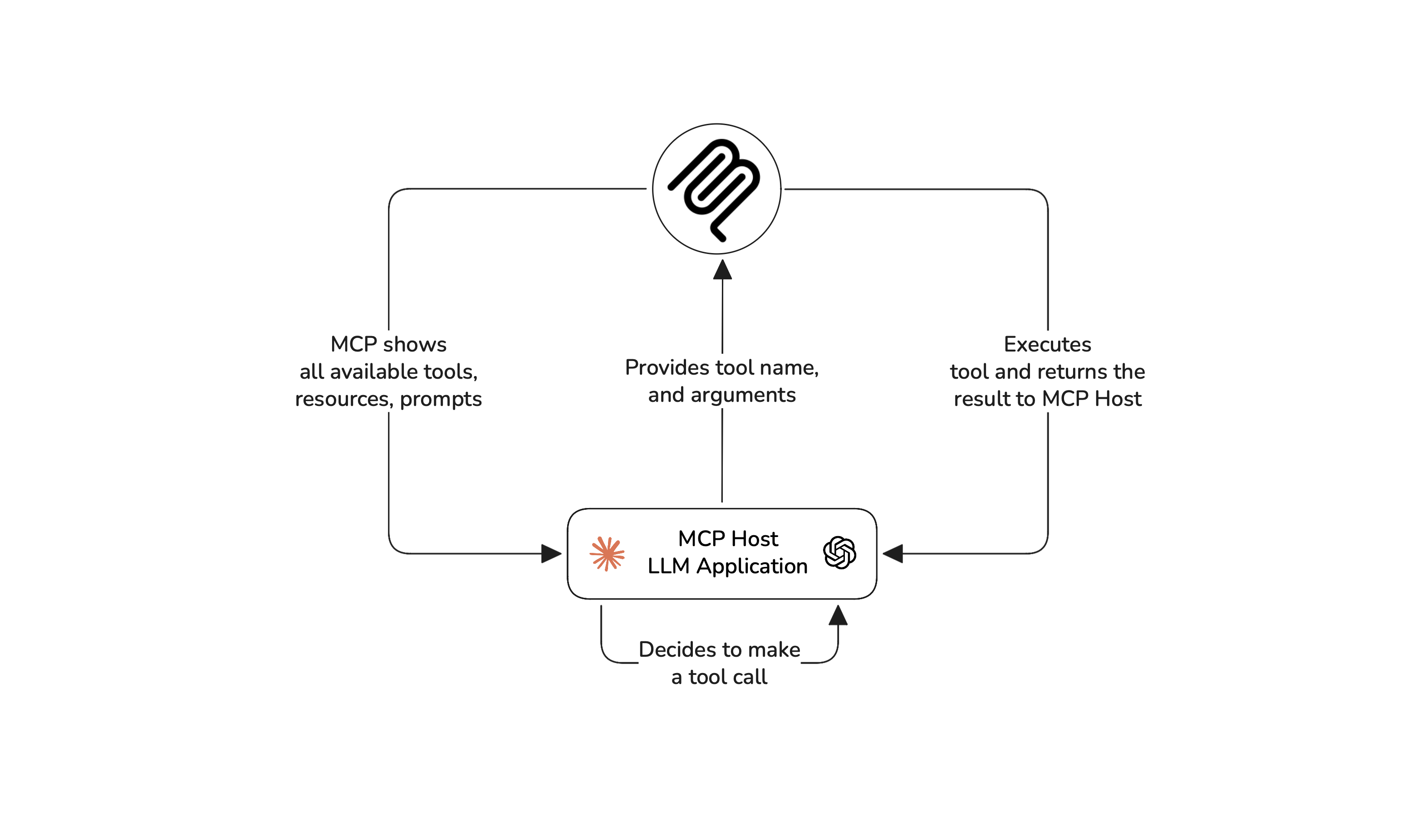
Because tools live on remote servers, you can connect an MCP server to any number of LLM apps, and vice versa. This makes MCP-based applications more flexible than regular AI agents with tools. Speaking of which, if you want to evaluate AI agents and not MCP applications, here’s a great article on how to evaluate AI agents.
The MCP architecture adds a layer of complexity to your LLM applications. To mitigate this, MCP provides a tool called the MCP Inspector to test servers and tools, but MCP evaluation isn’t just about testing servers, it’s about testing how the LLM application itself is working with the MCP.
The Eval Platform for AI Quality & Observability
Confident AI is the leading platform to evaluate AI apps on the cloud, powered by DeepEval.