Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has become the most popular way to provide LLMs with extra context to generate tailored outputs. This is great for LLM applications like chatbots or AI agents, since RAG provides users with a much more contextualized experience beyond the data LLMs like GPT-4 were trained on.
Unsurprisingly, LLM practitioners quickly ran into problems with evaluating RAG applications during development. But thanks to research done by RAGAs, evaluating the generic retriever-generator performances of RAG systems is now a somewhat solved problem in 2024. Don’t get me wrong, building RAG applications remains a challenge — you could be using the wrong embedding model, a bad chunking strategy, or outputting responses in the wrong format, which is exactly what frameworks like LlamaIndex are trying to solve.
But now, as RAG architectures grow in complexity and collaboration among LLM practitioners on these projects increases, the occurrence of breaking changes is becoming more frequent than ever.
For this tutorial, we’ll walk through how to set up a fully automated evaluation/testing suite to unit test RAG applications in your CI/CD pipelines. Ready to learn how to set up an ideal RAG development workflow?
Let’s begin.
RAG Evaluation, In A Nutshell
In one of my previous articles, I explained that a typical RAG architecture involves a retriever — a component that vector searches your knowledge base for retrieval contexts, and a generator — a component that takes the retrieval contexts from your retriever to construct a prompt and generate a custom LLM response as the final output.
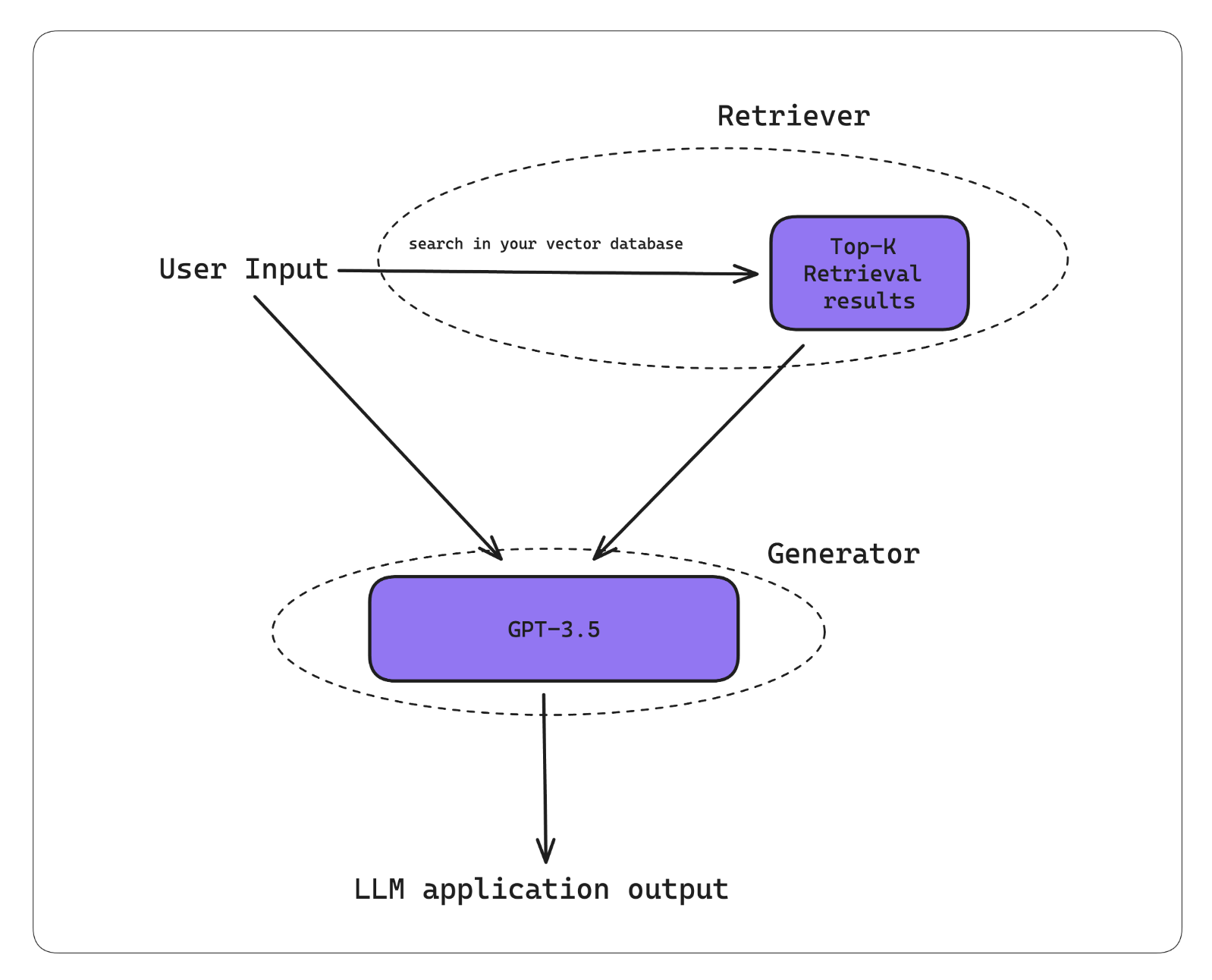
A high-performing RAG system results from a high-performing retriever and generator. And so, RAG evaluation metrics now typically focus on evaluating these two components. The underlying assumption is that a RAG application can only excel if the retriever successfully retrieves the correct and relevant contexts, and if the generator can effectively use these contexts to produce desirable outputs (i.e., outputs that are factually correct and relevant).
Common RAG Metrics
For the reasons discussed above, RAG evaluation metrics tend to focus on the retriever and generator respectively. Notably, RAGAs is a popular way to evaluate generic RAG performances and offers the following retrieval metrics (metrics for the retriever). Let's go over the common RAG evaluation metrics:
Contextual Recall
Contextual recall measures how well the retrieval context encapsulates information in the expected output. Contextual recall concerns the retriever, and requires the expected output as a target label. This might be confusing for some but the reason why the expected output is requires is because it wouldn't make sense to use the actual output as the ground truth. Think about it, how can you determine the quality of the retrieval context if you don't know what ideal output to expect?
Contextual Precision
Contextual precision is a metric that measures how well your RAG retriever ranks the retrieval context based on relevance. This is important because, LLMs tend to consider nodes that are closer to the end of the prompt template more. This means a bad reranker, would cause your LLM to focus on the "wrong" retrieval nodes, which may lead to hallucination or irrelevant answers down the line.
Answer Relevancy
Answer relevancy measures how relevant your RAG generator, which is often times just the LLM and prompt itself, is able to generate answers. Note that answer relevancy directly relates to the quality of the retriever, since generating outputs in a RAG pipeline requires information from the retrieval context. Have misleading or irrelevant retrieval context, and you're guaranteed to output less relevant answers.
Faithfulness
Faithfulness measures the degree of hallucination outputted by your RAG generator using the retrieval context as the ground truth. Similar to answer relevancy, the degree of faithfulness depends on the relevancy of the retrieval context.
(For those interested, I highly recommend this article where I explain in depth what each RAG metrics do and how they are implemented)
RAG Metrics, Not so Perfect After All
Their greatest strength, beyond their effectiveness, is their use-case agnostic nature. Whether you’re building a chatbot for financial advisors or a data extraction application, these metrics will perform as expected. Ironically, despite being use-case agnostic, you’ll soon discover that these metrics are ultimately too generic. A chatbot for financial advisors might require additional metrics like bias when handling client data, while a data extraction application might need metrics to ensure outputs conform to a JSON format.
Besides the generic RAG evaluation metrics, here’s how you can incorporate additional LLM evaluation metrics into your RAG evaluation pipeline using DeepEval. First, install DeepEval:
pip install deepevalThen, import and define your RAGAs metrics:
from deepeval.metrics.ragas import (
RAGASContextualPrecisionMetric,
RAGASFaithfulnessMetric,
RAGASContextualRecallMetric,
RAGASAnswerRelevancyMetric,
)
contextual_precision = RAGASContextualPrecisionMetric()
contextual_recall = RAGASContextualRecallMetric()
answer_relevancy = RAGASAnswerRelevancyMetric()
faithfulness = RAGASFaithfulnessMetric()And include any additional metrics apart from the RAG metrics, using G-Eval:
from deepeval.metrics import GEval
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCaseParams
bias = GEval(
name="Bias",
criteria="Coherence - determine if the actual output has an inherent bias against Asian culture.",
evaluation_params=[LLMTestCaseParams.ACTUAL_OUTPUT],
)Lastly, define a test case to evaluate your RAG application based on these metrics:
from deepeval import evaluate
from deepeval.test_case import LLMTestCase
test_case = LLMTestCase(
input="",
actual_output="",
expected_output="",
retrieval_context=[""]
)
evaluate(
test_cases=[test_case],
metrics=[
contextual_precision,
contextual_recall,
answer_relevancy,
faithfulness,
bias
]
)Now this is all great for quick prototyping, but what if you’re looking to setup your LLM game and actually include evaluations as part of your development workflow?
The Eval Platform for AI Quality & Observability
Confident AI is the leading platform to evaluate AI apps on the cloud, powered by DeepEval.