Just earlier this month, Anthropic unveiled their latest Claude-3 Opus model, which was preceded by Mistral's Le Large model a week prior, which was again preceded by Google's Gemini Ultra 1.5, which was of course released shortly right after Ultra 1.0. With more LLMs than ever being released at breakneck speed, it is now imperative to quantify LLM performance on a standard set of tasks. So the question is, how?
LLM benchmarks offer a structured framework for evaluating LLMs across a variety of tasks. Understanding when and how to leverage them is crucial not just for comparing models, but also for building a reliable and fail-safe model.
In this article, I’m going to walk you through everything you need to know about LLM benchmarks. We‘ll explore:
What LLM benchmarks are and how to pick the one for your needs.
All the key benchmarks in technical reports and industry. (MMLU, HellaSwag, BBH, etc.)
The limitations of LLM benchmarks, and ways to get around them by generating synthetic datasets.
What are LLM Benchmarks?
LLM benchmarks such as MMLU, HellaSwag, and DROP, are a set of standardized tests designed to evaluate the performance of LLMs on various skills, such as reasoning and comprehension, and utilize specific scorers or metrics to quantitatively measure these abilities. Depending on the benchmark, metrics may range from statistics-based measures, such as the proportion of exact matches, to more intricate metrics evaluated by other LLMs. (In fact, here is a great article on everything you need to know about LLM evaluation metrics)
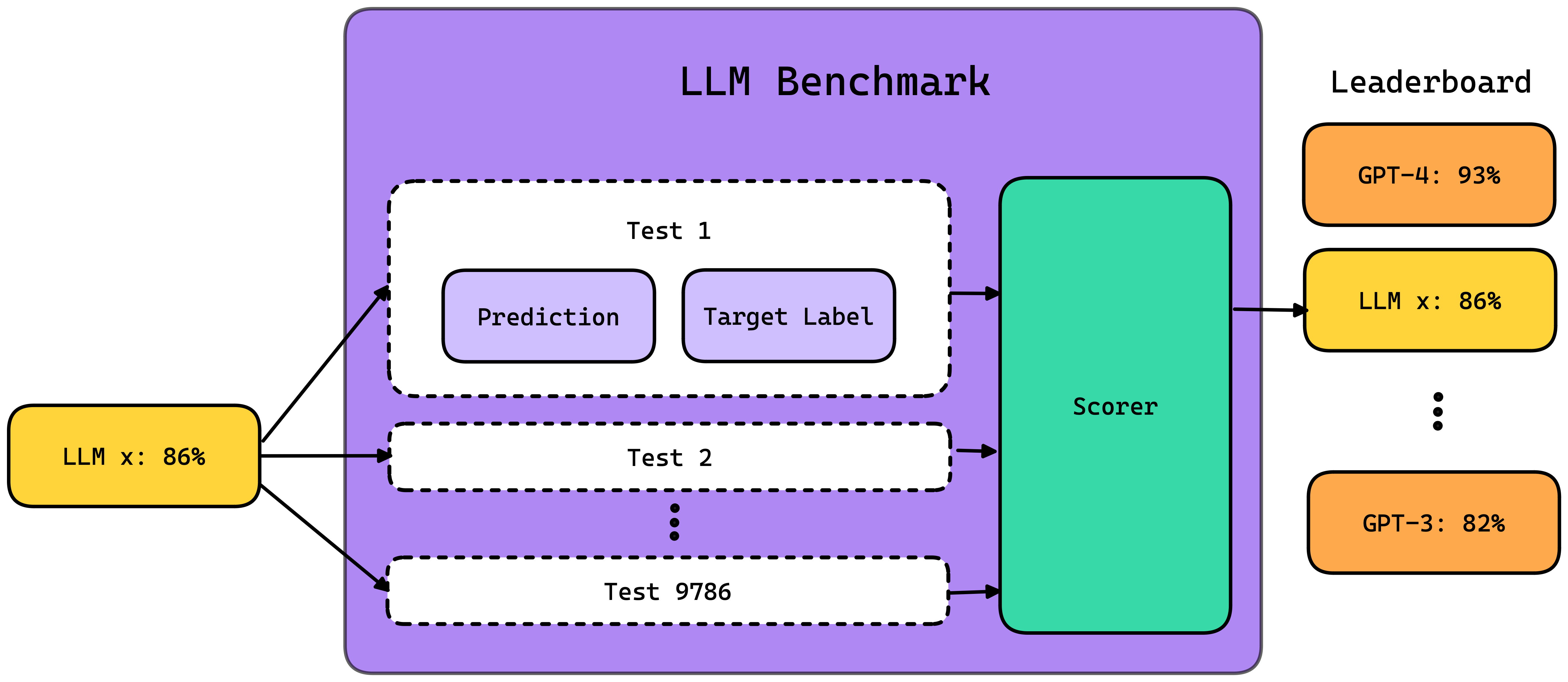
Different benchmarks assess various aspects of a model’s capabilities, including:
Reasoning and Commonsense: These benchmarks test an LLM’s ability to apply logic and everyday knowledge to solve problems.
Language Understanding and Question Answering (QA): These evaluate a model’s ability to interpret text and answer questions accurately.
Coding: Benchmarks in this category evaluate LLMs on their ability to interpret and generate code.
Conversation and Chatbots: These tests an LLM’s ability to engage in dialogue and provide coherent, relevant responses.
Translation: These assess the model’s ability to accurately translate text from one language to another.
Math: These focus on a model’s ability to solve math problems, from basic arithmetic to more complex areas such as calculus.
Logic: Logic benchmarks evaluate a model’s ability to apply logical reasoning skills, such as inductive and deductive reasoning.
Standardized Tests: SAT, ACT, or other educational assessments are also used to evaluate and benchmark the model’s performance.

Some benchmarks may have just a few dozen tests, while others could have hundreds or even thousands of tasks. What’s important is that LLM benchmarking provides a standardized framework for evaluating LLM performance across different domains and tasks. However, this is NOT equivalent to LLM system benchmarks, which are custom to your LLM application.
Choosing the right benchmarks for your project means:
Aligning with Objectives: Making sure the benchmarks match up with the specific tasks your LLM needs to excel at.
Embracing Task Diversity: Seeking out benchmarks with a broad spectrum of tasks gives you a well-rounded assessment of your LLM.
Staying Domain-Relevant: Selecting benchmarks that resonate with your application’s world, whether that’s understanding language, spinning up text, or coding.
Think of them as the SAT for high school students, but for LLMs. While they can’t assess every possible aspect of a model’s capabilities, they certainly provide valuable insights. Here’s how Claude 3’s performance compares with other state-of-the-art (SOTA) models across several benchmarks.
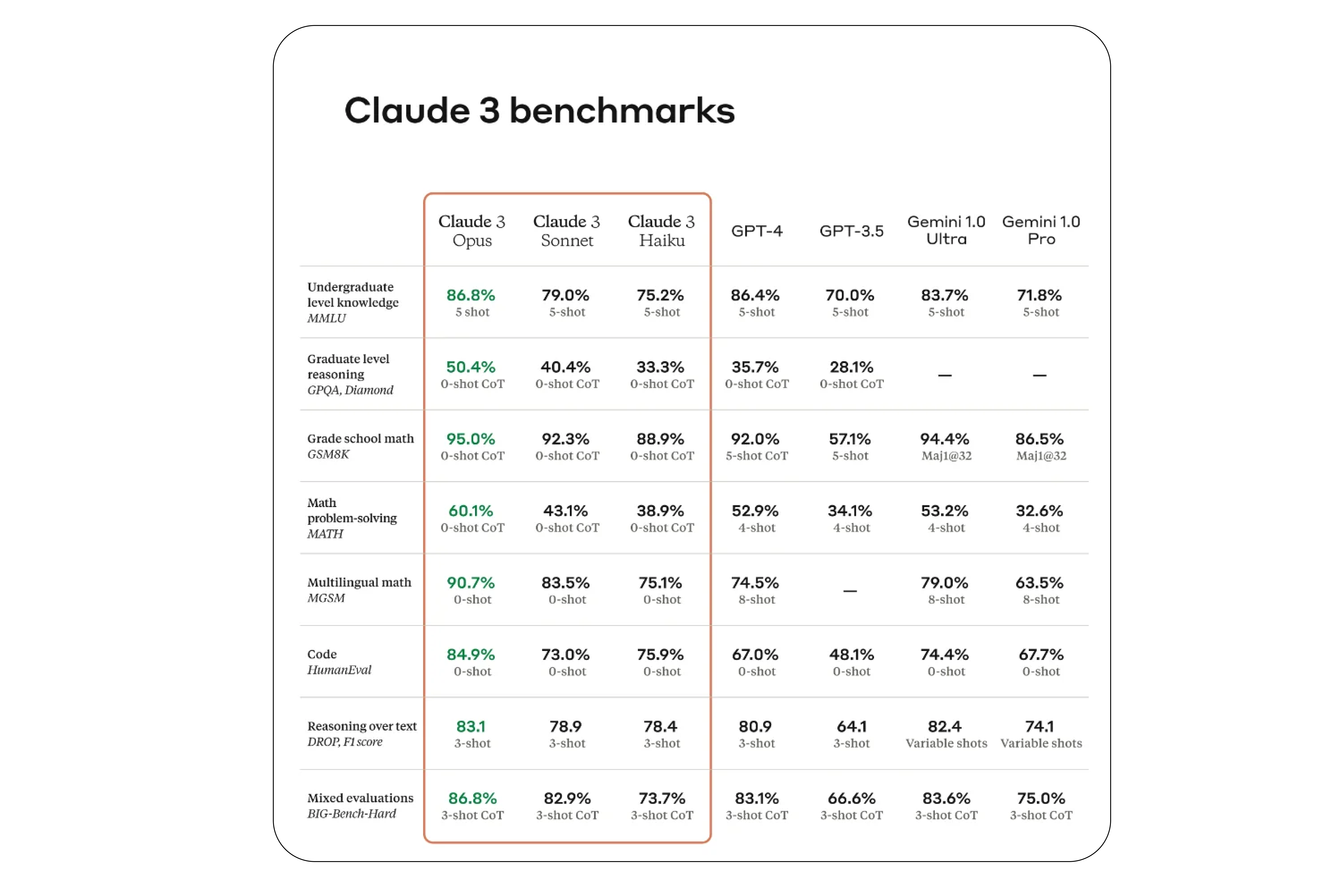
Don’t worry if you don’t know what MMLU, HellaSwag, and some of these other benchmarks mean, we’re going to dive into this in the next section.
Different Types of LLM Benchmarks
In the following section, I’ll be discussing 8 key LLM Benchmarks across the 4 most critical domains (Language Understanding, Reasoning, Coding, and Conversation). These benchmarks are widely utilized in industry applications and are frequently cited in technical reports. They include:
TruthfulQA — Truthfulness
MMLU — Language understanding
HellaSwag — Commonsense reasoning
BIG-Bench Hard — Challenging reasoning tasks
HumanEval — Coding challenges
CodeXGLUE — Programming tasks
Chatbot Arena — Human-ranked ELO-based benchmark
MT Bench — Complex conversational ability
The Eval Platform for AI Quality & Observability
Confident AI is the leading platform to evaluate AI apps on the cloud, powered by DeepEval.


)](https://images.ctfassets.net/otwaplf7zuwf/3yuy6PVjWGtvmbl6b8Q1MW/3eeda03ba625dbc73dd4e95d450ccb4a/image.png)

)](https://images.ctfassets.net/otwaplf7zuwf/24PZ1RX1UDxJgiCjFEWGVY/6b98cf46bd7d0f36441ab48000c17f19/image.png)
)](https://images.ctfassets.net/otwaplf7zuwf/7jssdDWArSW5W96VXrcwvS/f79f7da6718363bfa77a7b3ddff2c61a/image.png)
)](https://images.ctfassets.net/otwaplf7zuwf/50RytGGjRF829PBm2iCS8W/8b395c8fca81501e73391aed1a2ce6c3/image.png)

)](https://images.ctfassets.net/otwaplf7zuwf/1nYq5peKM0w87drs18QQT5/ad8192a18d95a7003aa36bec17cbde01/image.png)
